You can harvest (scan) metadata from data sources in the Metadata Manager. The scanned metadata is stored in a hierarchical manner (System > Environment > Table > Column) in the Data Catalog.
A System can contain multiple environments and in a typical data integration project a system can be a source or target type. You can create a system and specify data steward, system owner, and its business purpose etc.
Apart from creating systems, you can manage other system configurations using Metadata Options available in the top-right corner.
To create systems, follow these steps:
- Go to Application Menu > Data Catalog > Metadata Manager > Explore.
- In the Asset Catalog pane, click Metadata Options.
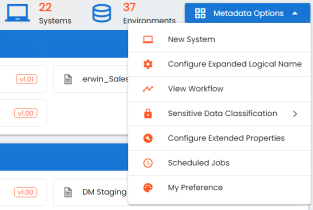
- Click New System.
- Enter appropriate values in the fields. Fields marked with a red asterisk are mandatory. Refer to the following table for field descriptions.
-
Source
-
Target
-
Both
- Click the Miscellaneous tab or click
 .
.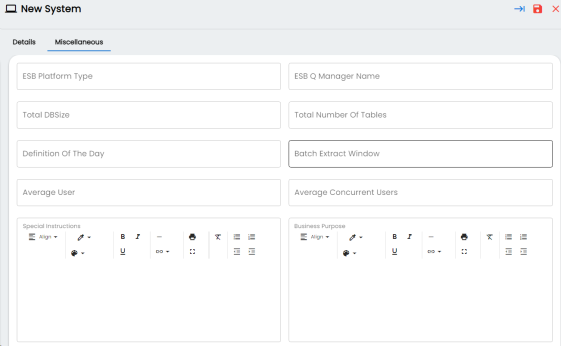
- Enter appropriate values in the fields. Fields marked with a red asterisk are mandatory. Refer to the following table for field descriptions.
- Click
 .
.
A new system is created.
The New System page appears.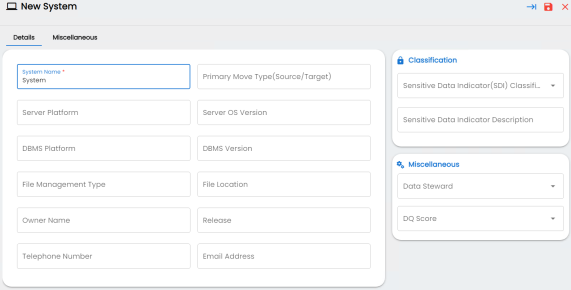
|
Field Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
System Name |
Specifies the physical name of the system. For example, Enterprise Data Warehouse. For more information on naming conventions, refer to the Best Practices section. |
|
Server Platform |
Specifies the server platform of the system. For example, Windows. |
|
DBMS Platform |
Specifies the DBMS platform of the system (if the system is an RDBMS source). For example, SQL Server. |
|
File Management Type |
Specifies the file management system (if the system is a file-based source). For example, MS Excel. |
|
Owner Name |
Specifies the full name of the system owner. For example, Talon Smith. |
|
Telephone Number |
Specifies the telephone number of the system owner. For example, 1-800-783-7946. |
|
Primary Move Type (Source/Target) |
Specifies whether the system is source, target, or both. Valid values are: |
|
Server OS version |
Specifies the OS version of the system's server. For example, Windows Server 2012 R2. |
|
DBMS Version |
Specifies the DBMS version of the system (if the system is an RDBMS source). For example, SQL Server 2017. |
|
File Location |
Specifies a file path (if the system is a file-based source). For example, C:\Users\Talon Smith\erwin\Mike - Target System |
|
Release |
Specifies the system release including the point release number. For example, Oracle 18c. |
|
Email Address |
Specifies the system owner's email address. For example, talon.smith@mauris.edu |
|
Sensitive Data Indicator (SDI) Classification |
Specifies the sensitivity classification of the system. Also, you can add multiple classifications to the system. For example, PHI, Confidential. For more information on configuring Sensitive Data Indicator (SDI) classifications, refer to the Configuring Sensitivity Classifications topic. |
|
Sensitive Data Indicator Description |
Specifies the description of the SDI classification. |
|
Data Steward |
Specifies the name of the data steward responsible for the system. For example, Jane Doe. Users assigned with the Legacy Data Steward role appear as drop down options. You can assign this role to a user in the Resource Manager. To assign data steward, select a data steward from the drop down options. |
|
DQ Score |
Specifies the overall data quality score of the system. For example, High (7-8). For more information on configuring DQ scores, refer to the Configuring Data Profiling and DQ Scores topic. |
|
Field Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ESB Platform Type |
Specifies the enterprise platform bus type (if the system is an ESB source). For example, Mule. |
|
ESB Q Manager Name |
Specifies the ESB queue manager's name of the system (if the source is an ESB). For example, John Doe. |
|
Total DBSize |
Specifies the total physical size of the database. For example, 198 GB. |
|
Total Number of Tables |
Specifies the total number of tables associated with the system. For example, 300. |
|
Definition of the Day |
Specifies the definition of the system at the end of the day. For example: Extraction of details from the source system is complete. |
|
Batch Extract Window |
Specifies the daily batch extract window of the system. For example: Batch extract from the source system is scheduled at 3:30 P.M. everyday. |
|
Average User |
Specifies the average number of system users. For example, 30. |
|
Average Concurrent Users |
Specifies the average number of concurrent system users. For example, 15. |
|
Special Instructions |
Specifies any special instructions or comments about the system. For example: The system acts as a source for creating the mapping specification. |
| Business Purpose |
Specifies the DBMS platform of the system (if the system is an RDBMS source). For example, SQL Server. |
Alternatively, before saving this system, you can add a new environment and configure the connections. To setup an environment, click ![]() to view the New Environment page.
to view the New Environment page.
Once the system is created, you can create environments and scan metadata from different database types.
You can enrich the system further by:
- Adding Documents
- Viewing Workflow Logs
- Associating Systems
- Configuring Expanded Logical Name of Tables/Columns
- Tagging Systems
You can manage a system as per your requirements. Managing systems involves:
- Editing or deleting systems
- Exporting systems information
|
Copyright © 2024 Quest Software Inc. |